Welcome to the first lecture of your Java basics journey! Before writing code, it’s important to understand the basic building blocks of programming. In this lecture, we will cover four key concepts:
Instruction, Program, Programming Language, and Code.
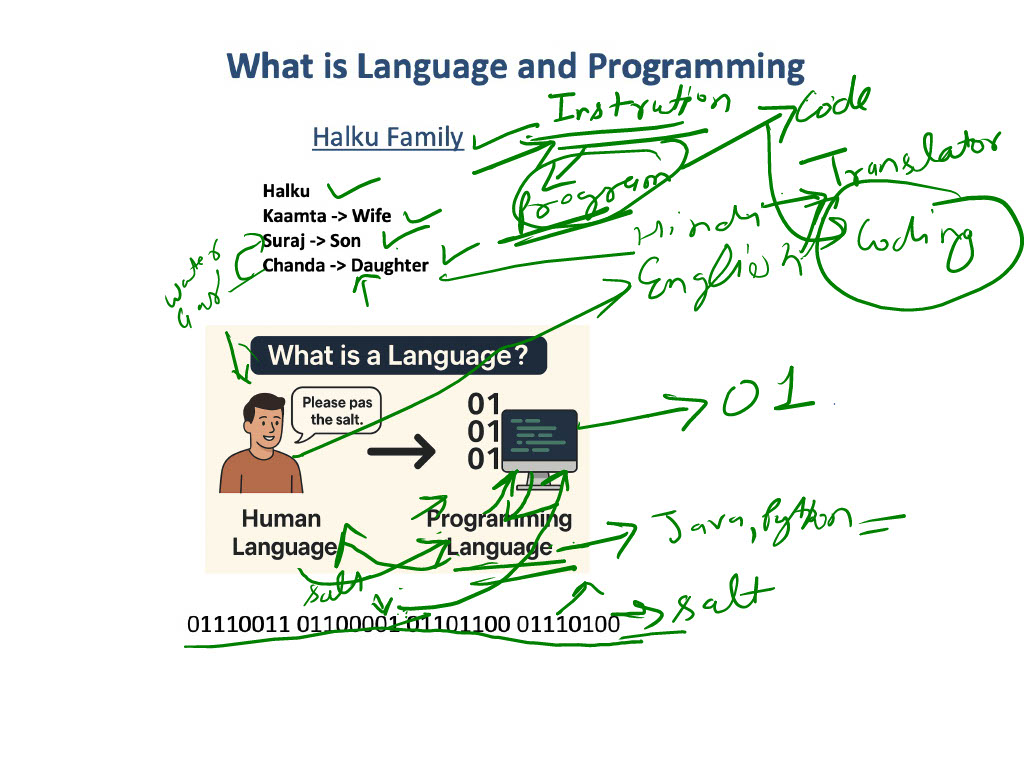
What is Programming?
Programming is the process of telling a computer what to do in a language it can understand.
Think of it like this:
- You know what you want to do.
- The computer doesn’t understand English, Hindi, or any human language.
- So, we use a programming language as a translator between our instructions and the computer.
In simple terms:
Programming = Giving instructions to the computer in a way it understands.
1. Instruction
An instruction is a single command or step that tells the computer exactly what to do.
Analogy: Step-by-step orders:
“Take the book from the table and place it on the shelf.”
Maggie Example:
Step: “Boil 1 cup of water.”
- This is one clear instruction.
- Each instruction tells the computer a small, specific task.
2. Program
A program is a collection of instructions written to perform a complete task.
Example: Calculating monthly expenses:
- Add salaries
- Subtract expenses
- Calculate balance
Program = A set of instructions that together achieve a goal.
Maggie Example: To cook Maggie:
- Boil 1 cup of water
- Add Maggie noodles
- Cook for 2 minutes
- Add tastemaker
- Mix and serve
All these steps together form a program — just like a program in Java combines instructions to complete a task.
3. Programming Language
A programming language is like a translator between you and the computer.
- You know what you want the computer to do.
- The computer only understands machine language (binary).
- The programming language lets you write human-readable instructions, which the computer can then execute.
Maggie Example:
- You know exactly how to cook Maggie.
- Your friend only understands English, and you are giving instructions in Hindi.
- You need a translator to convey your steps clearly.
Similarly, Java translates your instructions (code) into a language the computer can understand.
4. Code
Code is the actual text you write in a programming language.
- Each line of code represents an instruction.
- A program is made up of many lines of code.
Java Example:
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, Java!");
}
}- Each line is a piece of code.
- Together, they form a program that the computer can run.
Maggie Example:
public class MaggieRecipe {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Boil 1 cup of water");
System.out.println("Add Maggie noodles");
System.out.println("Cook for 2 minutes");
System.out.println("Add tastemaker");
System.out.println("Mix and serve");
}
}- Each System.out.println line is code.
- Together, all lines form a program — your computer now knows how to “cook Maggie”! 🍜
Watch On Youtube
Summary
| Concept | Meaning | Maggie Analogy |
| Instruction | A single step for the computer | Boil 1 cup of water |
| Program | A set of instructions to perform a task | Cooking Maggie from start to finish |
| Programming Language | Translator between humans and computers | Using English to explain Maggie recipe to computer |
| Code | Actual written instructions | Writing Maggie recipe steps in Java code |
Tip: Think of programming as giving clear instructions to a computer. The better your instructions (code) are organized, the easier it is for the computer to execute your tasks.

